Collection Interview Questions and Answers
Contents
- 1 What is Collection ? What is a Collections Framework ? What are the benefits of Java Collections Framework ?
- 2 What is the root interface in collection hierarchy ?
- 3 What is the difference between Collection and Collections ?
- 4 Which collection classes are synchronized or thread-safe ?
- 5 Name the core Collection interfaces ?
- 6 What is the difference between List and Set ?
- 7 What is the difference between Map and Set ?
- 8 What are the classes implementing List and Set interface ?
- 9 What is an iterator ?
- 10 What is the difference between Iterator and Enumeration ?
- 11 Which design pattern followed by Iterator ?
- 12 Which methods you need to override to use any object as key in HashMap ?
- 13 What is the difference between Queue and Stack ?
- 14 How to reverse the List in Collections ?
- 15 How to convert the array of strings into the list ?
- 16 What is the difference between ArrayList and Vector ?
- 17 What is the difference between HashMap and Hashtable ?
- 18 What is the difference between peek(),poll() and remove() method of the Queue interface ?
- 19 What is the difference between Iterator and ListIterator.
- 20 What is the difference between Array and ArrayList in Java ?
- 21 What is the difference between HashSet and TreeSet ?
- 22 What is the difference between HashMap and ConcurrentHashMap ?
- 23 Arrange the following in the ascending order (performance):HashMap , Hashtable , ConcurrentHashMap and Collections.SynchronizedMap
- 24 What is the difference between LinkedList and ArrayList in Java ?
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
What is Collection ? What is a Collections Framework ? What are the benefits of Java Collections Framework ?
Collection : A collection (also called as container) is an object that groups multiple elements into a single unit.
Collections Framework : Collections framework provides unified architecture for manipulating and representing collections.
Benefits of Collections Framework :
- Improves program quality and speed
- Increases the chances of reusability of software
- Decreases programming effort.
What is the root interface in collection hierarchy ?
Root interface in collection hierarchy is Collection interface . Few interviewer may argue that Collection interface extends Iterable interface. So iterable should be the root interface. But you should reply iterable interface present in java.lang package not in java.util package .It is clearly mentioned in Oracle Collection docs , that Collection interface is a member of the Java Collections framework. For Iterable interface Oracle doc , iterable interface is not mentioned as a part of the Java Collections framework .So if the question includes collection hierarchy , then you should answer the question as Collection interface (which is found in java.util package).
What is the difference between Collection and Collections ?
Collection is an interface while Collections is a java class , both are present in java.util package and part of java collections framework.
Which collection classes are synchronized or thread-safe ?
- Stack,
- Properties ,
- Vector,
- Hashtable
can be used in multi threaded environment because they are synchronized classes (or thread-safe).
Name the core Collection interfaces ?
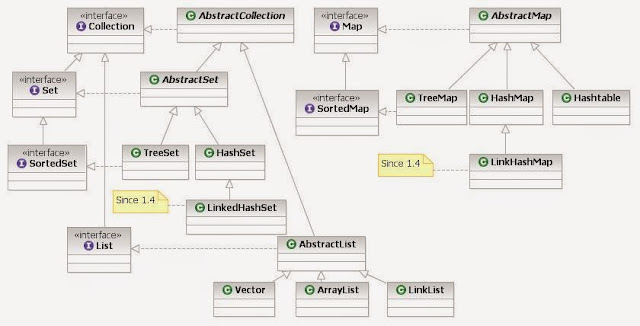
The list of core collection interfaces are : just mention the important ones
Important : Collection , Set , Queue , List , Map
Other interface also in the list : SortedSet, SortedMap , Deque, ListIterator etc.
What is the difference between List and Set ?
Set contain only unique elements while List can contain duplicate elements. Set is unordered while List is ordered . List maintains the order in which the objects are added .
What is the difference between Map and Set ?
Map object has unique keys each containing some value, while Set contain only unique values.
What are the classes implementing List and Set interface ?
Class implementing List interface : ArrayList , Vector , LinkedList ,
Class implementing Set interface : HashSet , TreeSet
What is an iterator ?
Iterator is an interface . It is found in java.util package. It provides methods to iterate over any Collection.
What is the difference between Iterator and Enumeration ?
The main difference between Iterator and Enumeration is that Iterator has remove() method while Enumeration doesn't. Hence , using Iterator we can manipulate objects by adding and removing the objects from the collections. Enumeration behaves like a read only interface as it can only traverse the objects and fetch it
Which design pattern followed by Iterator ?
It follows iterator design pattern. Iterator design pattern provides us to navigate through the collection of objects by using a common interface without letting us know about the underlying implementation.
Enumeration is an example of Iterator design pattern.
Which methods you need to override to use any object as key in HashMap ?
To use any object as key in HashMap , it needs to implement equals() and hashCode() method .
What is the difference between Queue and Stack ?
Queue is a data structure which is based on FIFO ( first in first out ) property . An example of Queue in real world is buying movie tickets in the multiplex or cinema theaters.
Stack is a data structure which is based on LIFO (last in first out) property . An example of Stack in real world is insertion or removal of CD from the CD case.
How to reverse the List in Collections ?
There is a built in reverse method in Collections class . reverse(List list) accepts list as parameter.
Collections.reverse(listobject);How to convert the array of strings into the list ?
Arrays class of java.util package contains the method asList() which accepts the array as parameter. So,
String[] wordArray = {"Love Yourself" , "Alive is Awesome" , "Be in present"};
List wordList = Arrays.asList(wordArray);What is the difference between ArrayList and Vector ?
It is one of the frequently asked collection interview question , the main differences are Vector is synchronized while ArrayList is not . Vector is slow while ArrayList is fast . Every time when needed, Vector increases the capacity twice of its initial size while ArrayList increases its ArraySize by 50%.
What is the difference between HashMap and Hashtable ?
It is one of the most popular collections interview question for java developer . Make sure you go through this once before appearing for the interview . Main differences between HashMap and Hashtable are :
- HashMap allows one null key and any number of null values while Hashtable does not allow null keys and null values.
- HashMap is not synchronized or thread-safe while Hashtable is synchronized or thread-safe .
What is the difference between peek(),poll() and remove() method of the Queue interface ?
Both poll() and remove() method is used to remove head object of the Queue. The main difference lies when the Queue is empty(). If Queue is empty then poll() method will return null . While in similar case , remove() method will throw NoSuchElementException . peek() method retrieves but does not remove the head of the Queue. If queue is empty then peek() method also returns null.
What is the difference between Iterator and ListIterator.
Using Iterator we can traverse the list of objects in forward direction . But ListIterator can traverse the collection in both directions that is forward as well as backward.
What is the difference between Array and ArrayList in Java ?
This question checks whether student understand the concept of static and dynamic array. Some main differences between Array and ArrayList are :
- Array is static in size while ArrayList is dynamic in size.
- Array can contain primitive data types while ArrayList can not contain primitive data types.
What is the difference between HashSet and TreeSet ?
Main differences between HashSet and TreeSet are :
- HashSet maintains the inserted elements in random order while TreeSet maintains elements in the sorted order
- HashSet can store null object while TreeSet can not store null object.
What is the difference between HashMap and ConcurrentHashMap ?
This is also one of the most popular java collections interview question . Make sure this question is in your to do list before appearing for the interview . Main differences between HashMap and ConcurrentHashMap are : a. HashMap is not synchronized while ConcurrentHashMap is synchronized. b. HashMap can have one null key and any number of null values while ConcurrentHashMap does not allow null keys and null values .
Arrange the following in the ascending order (performance):HashMap , Hashtable , ConcurrentHashMap and Collections.SynchronizedMap
Hashtable < Collections.SynchronizedMap < ConcurrentHashMap < HashMap
What is the difference between LinkedList and ArrayList in Java ?
Main differences between LinkedList and ArrayList are :
- LinkedList is the doubly linked list implementation of list interface , while , ArrayList is the resizable array implementation of list interface.
- LinkedList can be traversed in the reverse direction using descendingIterator() method provided by the Java Api developers , while , we need to implement our own method to traverse ArrayList in the reverse direction .